If you’re new to writing or learning English, understanding modal verbs is essential in crafting clear, engaging, and powerful content. These auxiliary verbs are used to express possibility, ability, permission, and obligation. In this beginner’s guide, we will introduce the basic modal verbs, their functions, and simple tips for using them effectively in your writing.
- The Nine Core Modal Verbs:
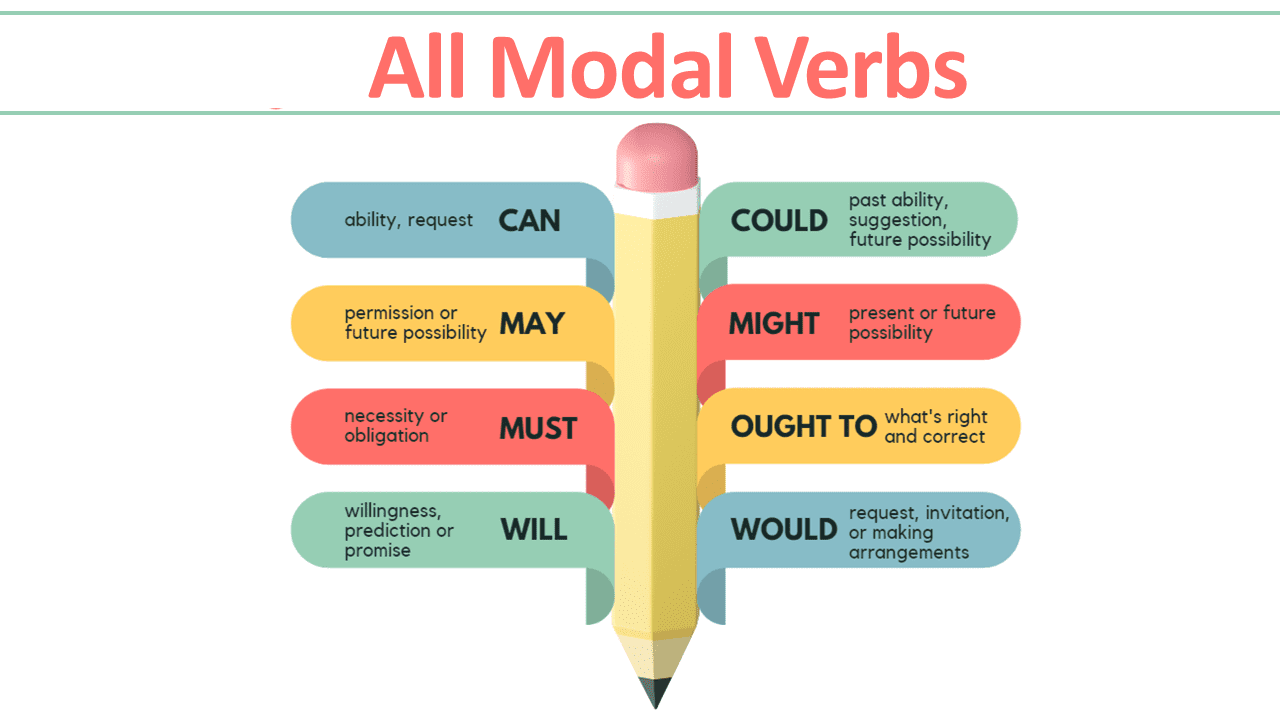
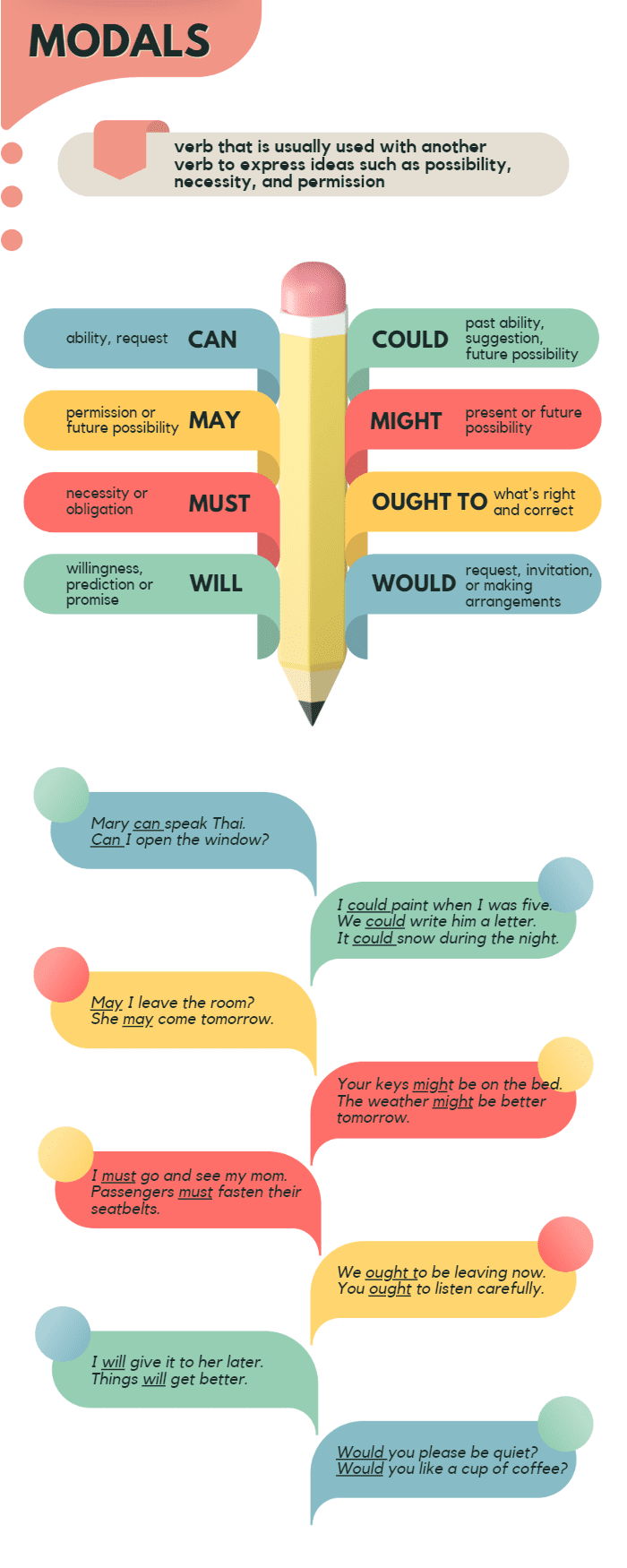
Modal verbs are a small but important group of verbs in the English language. There are nine primary modal verbs: can, could, may, might, will, would, shall, should, and must. Here’s a quick overview of each modal verb’s primary use:
- Can: Expresses ability or possibility.
- Could: Represents a polite or tentative version of ‘can’ or a hypothetical situation.
- May: Conveys permission or a possibility.
- Might: Indicates a weaker possibility or uncertainty.
- Will: Refers to future events or decisions.
- Would: Relates to hypothetical situations, preferences, or past habits.
- Shall: Used in formal situations to discuss future plans or seek advice.
- Should: Suggests advice, recommendation, or obligation.
- Must: Denotes a strong obligation or necessity.
| Modal Verb | Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Can | Ability or possibility | I can speak three languages. |
| Request | Can you lend me your book? | |
| Could | Polite or tentative version of ‘can’ | Could you spare a minute to chat? |
| Hypothetical or past ability | He could run a mile in under six minutes when he was younger. | |
| May | Permission | May I have a glass of water? |
| Possibility | The weather may improve in the afternoon. | |
| Might | Weaker possibility or uncertainty | I might join the gym next month. |
| Will | Future events or decisions | I will visit my grandparents this weekend. |
| Making promises | I will finish the report by tomorrow. | |
| Would | Hypothetical situations or preferences | I would travel more if I had the time. |
| Polite requests | Would you mind opening the window? | |
| Shall | Future plans (formal) | We shall discuss the proposal on Monday. |
| Asking for advice (formal) | Shall I book a table at the restaurant? | |
| Should | Advice, recommendation, or obligation | You should wear sunscreen when going outside. |
| Expectation | The package should arrive tomorrow. | |
| Must | Strong obligation or necessity | You must submit your assignment on time. |
| Strong probability or logical conclusion | She must be tired after working all day. |
Uses of Modal Verbs in Sentences
- Can a. Ability
- She can play the violin beautifully.
- He can solve complex mathematical problems.
- The dog can perform amazing tricks.
b. Possibility
- There can be unexpected challenges when learning a new skill.
- The meeting can run late if there are many questions.
- The package can arrive early if the courier is fast.
c. Request
- Can you lend me your charger?
- Can I borrow your book for the weekend?
- Can you pass me the remote control, please?
- Could a. Polite Request
- Could you please give me a hand with this task?
- Could I have some more water, please?
- Could you let me know when you’re available?
b. Past Ability
- When she was younger, she could lift 200 pounds.
- He could run a mile in under five minutes in high school.
- They could speak multiple languages as children.
c. Hypothetical Situation
- If we leave now, we could still catch the last train.
- We could save more money if we cut down on eating out.
- She could earn a promotion if she works hard.
- May a. Permission
- May I use your restroom?
- May I have a slice of cake?
- May I join you for lunch?
b. Possibility
- The weather forecast says it may snow tomorrow.
- They may decide to move to a different city.
- The bus may be delayed due to traffic.
- Might a. Weaker Possibility
- They might go on a vacation next month.
- It might rain later this evening.
- The store might have the item I’m looking for.
b. Suggestion
- If you’re tired, you might want to take a break.
- You might enjoy the new movie that just came out.
- She might find it helpful to talk to a career counselor.
- Will a. Future Events
- I will graduate from college next year.
- The conference will take place in June.
- The new store will open next month.
b. Decisions
- She will decide on her career path after the internship.
- I will choose a new laptop this weekend.
- They will pick a wedding venue by the end of the month.
c. Promises
- I will always be here for you.
- We will keep your personal information confidential.
- He will return your book as soon as he finishes reading it.
- Would a. Hypothetical Situations
- If I won the lottery, I would buy a new house.
- She would travel the world if she had more time.
- They would start their own business if they had the capital.
b. Preferences
- I would prefer tea over coffee.
- He would rather work from home than commute to the office.
- They would choose a quiet vacation over a busy city trip.
c. Polite Requests
- Would you kindly help me set up the table?
- Would you mind giving me a ride to the airport?
- Would you please turn down the volume on the television?
- Shall
a. Future Plans – Formal- We shall commence the meeting at 10 AM.
- The ceremony shall take place outdoors.
- The presentation shall be delivered next week.
b. Asking for Advice –
b. Asking for Advice – Formal
– Shall I bring some snacks to the party?
– Shall we book a table for dinner tonight?
– Shall I prepare a report on the project’s progress?
- Should
a. Advice- You should try the new restaurant down the street.
- He should exercise regularly to stay healthy.
- They should study for their exams in advance.
b. Recommendation
- They should consult a doctor before taking any medication.
- You should invest in a high-quality laptop for better performance.
- She should practice speaking the language before her trip.
c. Expectation
- The delivery should arrive by noon.
- The project should be completed within the next two weeks.
- The sun should come out later in the afternoon.
- Must
a. Strong Obligation- All employees must attend the mandatory training session.
- Passengers must fasten their seat belts during takeoff and landing.
- You must submit your assignment on time.
b. Necessity
- We must protect the environment for future generations.
- She must meet the deadline to keep her job.
- He must save enough money for his retirement.
c. Logical Conclusion
- Given her reaction, she must have been surprised by the news.
- He must be exhausted after his long journey.
- The crowd’s cheers must have boosted the team’s morale.