A noun phrase is a group of words that functions as a noun in a sentence. It consists of a head noun, which is the main word that gives the phrase its meaning, and other words that modify or complement the head noun. These modifiers can include articles, adjectives, prepositional phrases, and other nouns. Noun phrases can vary in complexity and length, and they play a crucial role in providing more information about the subject or object in a sentence. Examples of noun phrases include “the tall building,” “a red apple,” and “my favorite book.”
Examples of Noun Phrase:
- The curious cat
- A cozy blanket
- Several colorful balloons
- My younger sister
- The old oak tree in the backyard
- An interesting book on science
- The bustling city streets
- A delicious slice of chocolate cake
- Three playful puppies
- A beautiful painting by the artist
- His loud laughter
- The small, wooden table
- Many students in the classroom
- The ancient ruins of Rome
- A group of excited children
- The bright morning sun
- The silver necklace around her neck
- The charming old village
- A cup of hot tea
- The fascinating history lesson
Structure of a Noun Phrase
The structure of a noun phrase (NP) in a sentence typically follows a pattern that includes a head noun along with various modifiers and additional elements. Here’s an example sentence illustrating the structure:
Example Sentence: “The black cat with green eyes that I adopted from the shelter is quite playful.”
Structure Breakdown:
- Head Noun: “Cat”
- Determiners: “The”
- Adjectives: “Black,” “Green,” “Playful”
- Relative Clause: “That I adopted from the shelter”
- Prepositional Phrase: “With green eyes,” “From the shelter”
In this example, the head noun is “cat,” and the entire phrase “the black cat with green eyes that I adopted from the shelter” functions as a noun phrase. The modifiers provide additional details about the cat, and the relative clause adds more information about the adoption. Prepositional phrases offer further context.
Function of Noun Phrases:
Noun phrases play various roles in a sentence, serving as:
- Subject: The cat slept peacefully.
- Object: She fed her dog.
- Complement: He is a skilled artist.
- Object of a Preposition: She sat on the chair.
- Appositive: My friend, an excellent cook, prepared dinner.
- Direct Address: John, pass the salt.
These functions demonstrate the versatility of noun phrases in conveying different grammatical roles within sentences.
Position of Noun Phrases:
The position of a noun phrase in a sentence refers to where it is located within the sentence structure. It usually consists of a noun and its modifiers. The noun phrase can be found in various positions, including the subject, object, or complement, depending on its role in the sentence.
- Example Sentence: The diligent student always completes assignments on time.
In this example, “The diligent student” is the noun phrase and is positioned as the subject of the sentence.
Modifiers in Noun Phrases:
Modifiers in noun phrases are words or groups of words that provide additional information about the noun. They include adjectives, articles (a, an, the), possessive nouns, quantifiers (such as some, many), and prepositional phrases. These modifiers enhance the details, describe ownership, specify quantity, or indicate location, making the noun more precise and informative in a sentence.
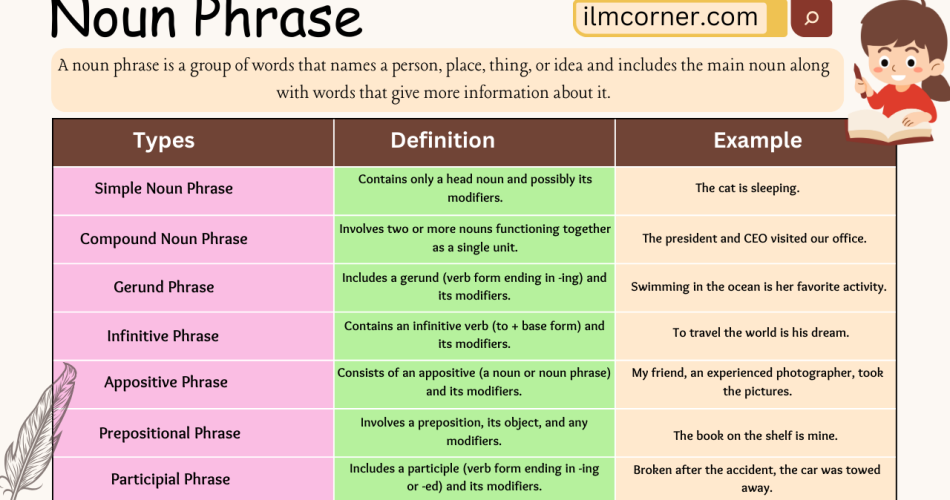
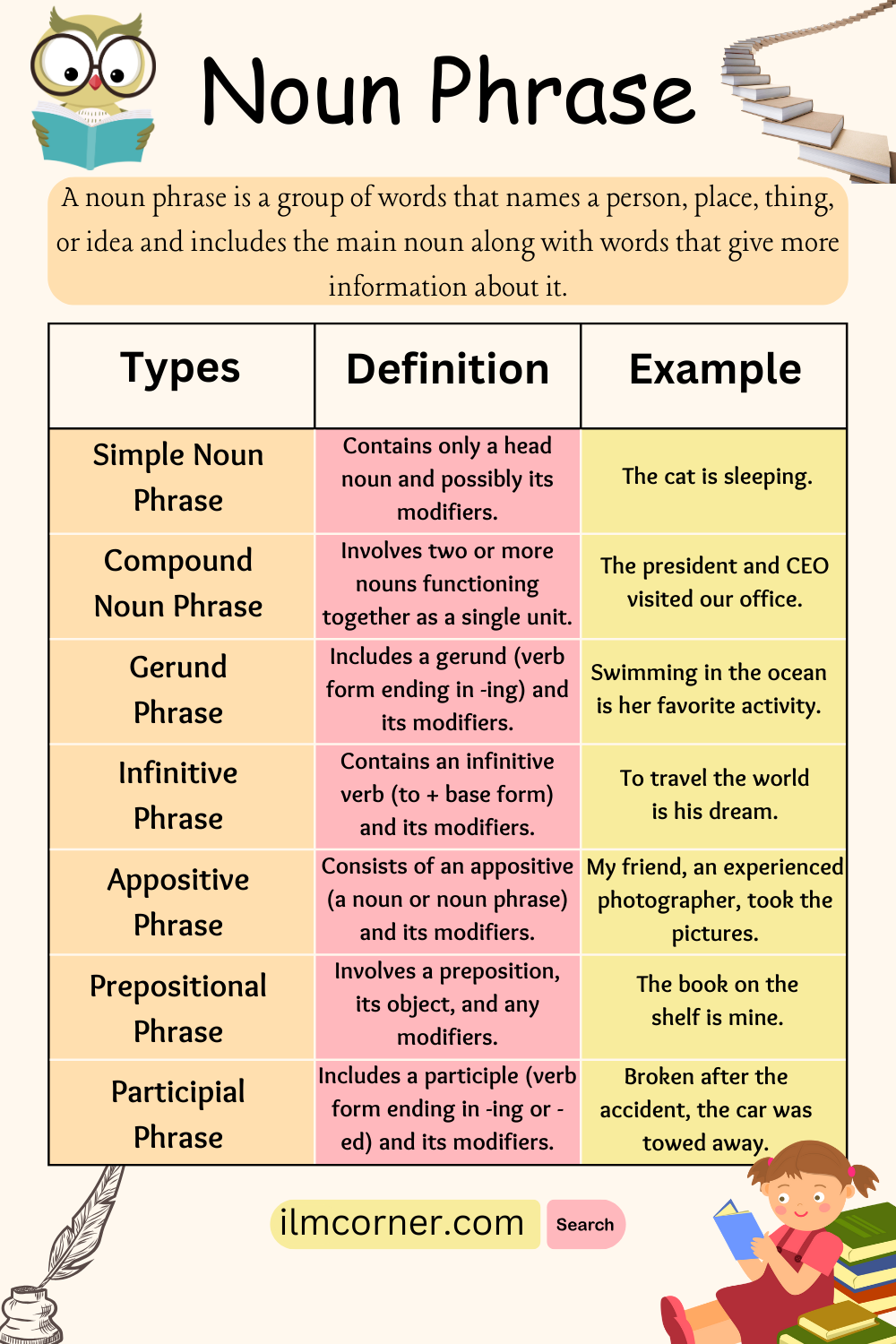
Types of a Noun Phrase:
Noun phrases can be categorized into various types based on their functions and structures. Here are some common types:
- Simple Noun Phrase:
- Contains only a head noun and possibly its modifiers.
- The cat is sleeping.
- Contains only a head noun and possibly its modifiers.
- Compound Noun Phrase:
- Involves two or more nouns functioning together as a single unit.
- The president and CEO visited our office.
- Involves two or more nouns functioning together as a single unit.
- Gerund Phrase:
- Includes a gerund (verb form ending in -ing) and its modifiers.
- Swimming in the ocean is her favorite activity.
- Includes a gerund (verb form ending in -ing) and its modifiers.
- Infinitive Phrase:
- Contains an infinitive verb (to + base form) and its modifiers.
- To travel the world is his dream.
- Contains an infinitive verb (to + base form) and its modifiers.
- Appositive Phrase:
- Consists of an appositive (a noun or noun phrase) and its modifiers.
- My friend, an experienced photographer, took the pictures.
- Consists of an appositive (a noun or noun phrase) and its modifiers.
- Prepositional Phrase:
- Involves a preposition, its object, and any modifiers.
- The book on the shelf is mine.
- Involves a preposition, its object, and any modifiers.
- Participial Phrase:
- Includes a participle (verb form ending in -ing or -ed) and its modifiers.
- Broken after the accident, the car was towed away.
- Includes a participle (verb form ending in -ing or -ed) and its modifiers.
- Nominalized Phrase:
- Involves a verb or an adjective that functions as a noun.
- The investigation led to several arrests. (“Investigation” acts as a nominalized phrase.)
- Involves a verb or an adjective that functions as a noun.