A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, idea, or quality in a sentence. It serves as the subject, object, or complement in a sentence and can be classified into various types based on their characteristics.
Here are a few examples of nouns:
- Teacher (common noun)
- Mountain (common noun)
- Happiness (abstract noun)
- Bicycle (concrete noun)
- New York City (proper noun)
- Team (collective noun)
- Sunshine (compound noun)
Let’s dive a little deeper and learn more about types of nouns.
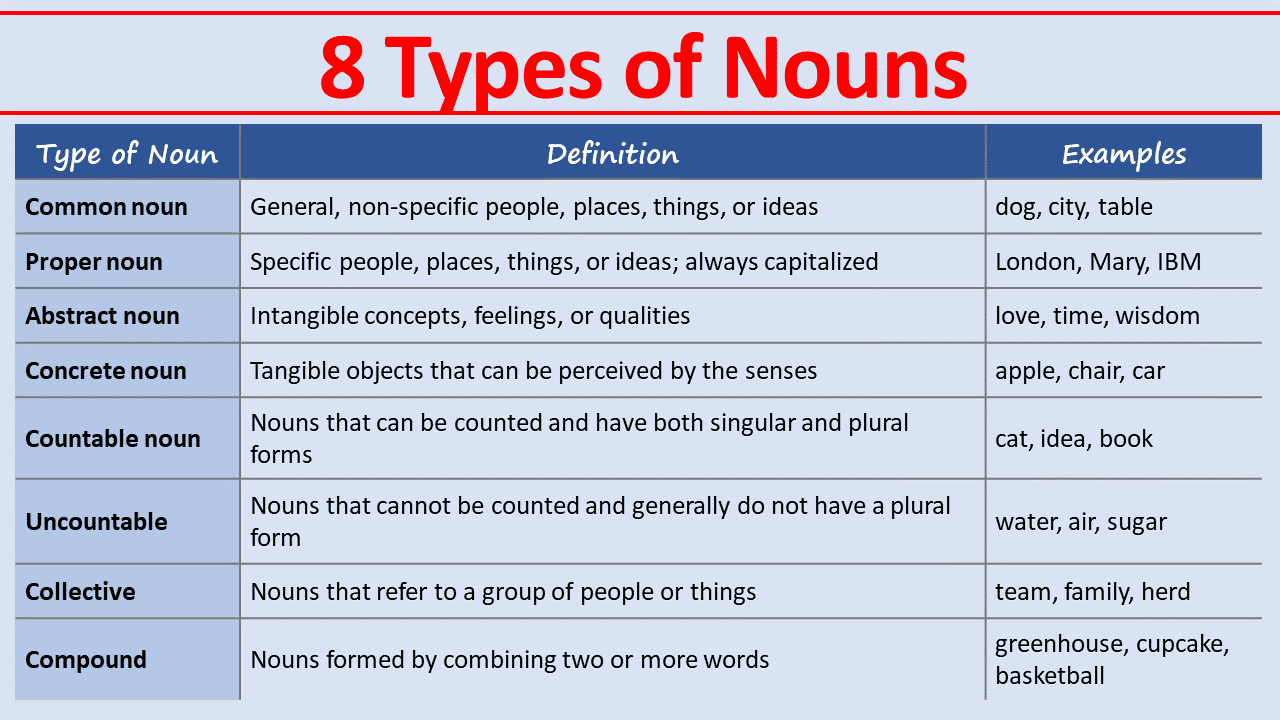
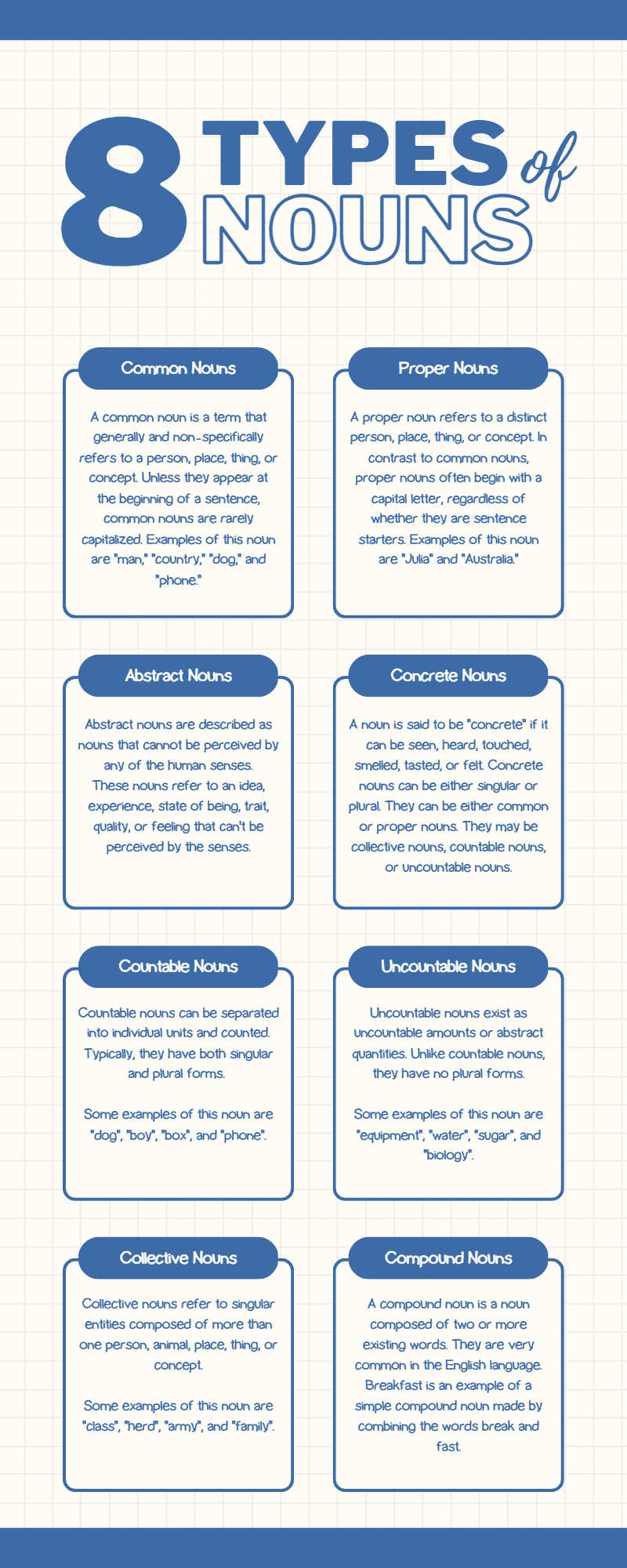
There are several types of nouns in the English language. Here are eight types, along with examples and sentence analyses for each:
- Common nouns: These nouns refer to general, non-specific people, places, things, or ideas. They are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence.
Examples: dog, city, love
Sentence: The dog chased the ball in the park.
Analysis: “dog” (common noun) is the subject, “ball” (common noun) is the object, and “park” (common noun) is part of the prepositional phrase. - Proper nouns: These nouns refer to specific people, places, things, or ideas and are always capitalized.
Examples: London, Shakespeare, Nike
Sentence: Julie visited London last summer.
Analysis: “Julie” (proper noun) is the subject, and “London” (proper noun) is part of the prepositional phrase. - Abstract nouns: These nouns represent intangible concepts, feelings, or qualities.
Examples: happiness, time, knowledge
Sentence: Knowledge is power.
Analysis: “Knowledge” (abstract noun) is the subject, and “power” (abstract noun) is the predicate nominative. - Concrete nouns: These nouns represent tangible objects that can be perceived by the senses.
Example: apple, chair, beach
Sentence: She left her chair on the beach.
Analysis: “She” (pronoun) is the subject, “chair” (concrete noun) is the direct object, and “beach” (concrete noun) is part of the prepositional phrase. - Countable nouns: These nouns can be counted and have both singular and plural forms.
Examples: car, book, idea
Sentence: I borrowed three books from the library.
Analysis: “I” (pronoun) is the subject, and “books” (countable noun) is the direct object. - Uncountable nouns: These nouns cannot be counted and generally do not have a plural form.
Examples: water, information, air
Sentence: She needs more information before making a decision.
Analysis: “She” (pronoun) is the subject, and “information” (uncountable noun) is the direct object. - Collective nouns: These nouns refer to a group of people or things.
Examples: team, family, flock
Sentence: The team is meeting in the conference room.
Analysis: “team” (collective noun) is the subject, and “conference room” (common noun) is part of the prepositional phrase. - Compound nouns: These nouns are formed by combining two or more words.
Examples: skateboard, toothpaste, greenhouse
Sentence: The gardener placed the plants in the greenhouse.
Analysis: “gardener” (common noun) is the subject, “plants” (common noun) is the direct object, and “greenhouse” (compound noun) is part of the prepositional phrase.
A paragraph on Types of nouns analysis
Last week, my sister (common noun) and I visited the Grand Canyon (proper noun). The breathtaking beauty (abstract noun) of this natural wonder left us in awe. We hiked along the South Rim (proper noun), admiring the canyon’s (common noun) colorful layers and impressive depth. The birds (collective noun) soaring above the canyon walls added to the tranquil atmosphere. Our unforgettable adventure (compound noun) in the Grand Canyon (proper noun) will always remain a cherished memory (abstract noun).